By analyzing imports, exports, freight rates, and transit times, this feature equips businesses, logistics professionals, and analysts with the information needed to optimize supply chain operations and plan trade routes efficiently.
This article delves into the Trade and Transit feature, explaining its components and how to leverage it for effective decision-making.
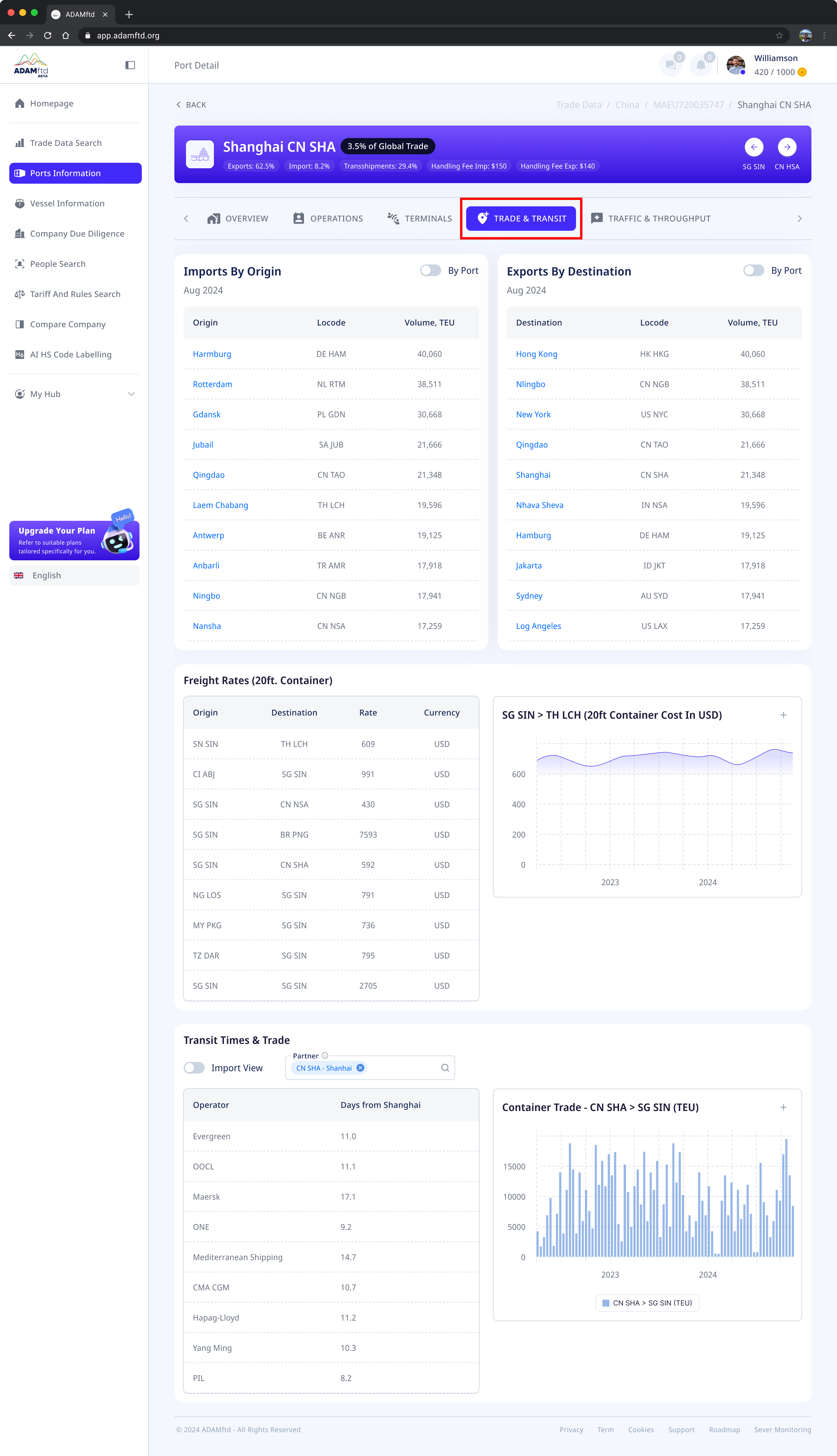
1. Imports by Origin and Exports by Destination
- Imports by Origin:
- Lists the top origin ports sending goods to the selected port.
- Shows the volume of imported goods in TEUs (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Units).
- Includes the locode (location code) of each origin port.
- Exports by Destination:
- Lists the primary destination ports served by the selected port.
- Displays export volumes in TEUs along with their locodes.
Importance
- Provides insights into the port’s primary trade partners, both for imports and exports.
- Helps businesses identify key trade hubs and evaluate market opportunities.
2. Freight Rates
- Freight rates for 20ft containers:
- Details the cost of shipping containers between the selected port and various destinations or origins.
- Includes rates in the specified currency (e.g., USD).
- Graphical trends:
- Visualizes historical changes in freight rates for selected routes.
Importance
- Allows users to analyze shipping costs and select cost-effective routes.
- Provides insights into freight market trends for better financial planning.
3. Transit Times and Trade
- Transit times:
- Lists the average number of days it takes for different shipping operators to transport goods from the selected port to specified destinations or vice versa.
- Container trade volume trends:
- Graphs showing historical container trade volumes for specific routes (e.g., Shanghai to Singapore).
Importance
- Helps users select shipping operators based on transit time efficiency.
- Provides visibility into trade volume trends, aiding in capacity planning and forecasting.
4. Key Features and Filters
Features
- Toggle between import and export views: Focus on either inbound or outbound trade data.
- Partner-specific analysis: Filter data by specific trade partners to analyze bilateral trade relationships.
Importance
- Allows for tailored analysis based on specific business needs.
- Simplifies trade data navigation and enhances decision-making efficiency.